Diseases can come from anywhere, even from the
food you eat. Without your knowledge, in certain foods there is bacteria that
may infect, causing disease and even risk of death.
Here are 7 bacteria in food that can cause
disease:
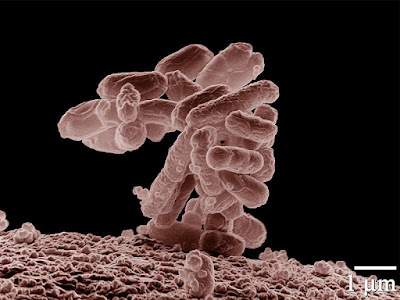
1. E. coli Bacteria
Escherichia coli bacteria live in the
gut of humans and other mammals like cows, sheep and goats. These bacteria are
often found in half cooked meat, raw milk and contaminated water.
Symptoms of bacterial infections caused by E.
coli are severe diarrhea, abdominal pain and vomiting that can last up to 5 to
10 days. Even so, most of the infections caused by bacteria E. coli is
relatively harmless, but certain types such as E. coli O157: H7 can causing
bloody diarrhea, kidney failure and even death.
To prevent bacterial infection caused by E.
coli, cook until meat well cooked, wash fruits and vegetables before eating or
cooking, and avoid consuming raw milk and unpasteurized.
2. Campylobacter
Campylobacter is a spiral-shaped bacterium and
grew to infect chickens and cows without signs of disease. Most people infected
with this bacteria will usually get diarrhea, cramping, abdominal pain,
and fever within 2-5 days after exposure from bacteria.
Diarrhea are likely to bleed and can be
accompanied by nausea and vomiting, usually last about a week.
According to WHO, campylobacteriosis cases or Campylobacter
infection is generally mild, but the bacteria can be fatal in children are very
young, the elderly and people who have impaired immune systems.
The way to prevent Campylobacter infection is
to cook the meat until well cooked, wash hands and clean all kitchen equipment
after cutting meat, and drink only milk that has been pasteurized.
3. Listeria
Listeria monocytogenes is a bacterium found in
soil and water, but it also found in raw foods and processed foods and
unpasteurized milk. Not like other bacteria, Listeria can grow and reproduce
even in cold refrigerator.
Symptoms of Listeria infection include fever,
chills, headache, abdominal pain and vomiting. But for some people, the disease
can become more serious and even fatal, ie pregnant women, adults over the age
of 50, and people with weakened immune systems.
To prevent Listeria infection, wash vegetables
and fruits such as melons and cucumbers until clean before consumption. If the
meat liquid spilled on the refrigerator, wipe spills immediately to prevent the
proliferation and spread of the bacteria Listeria.
4. Vibrio
Vibrio parahaemolyticus bacteria live in salt
water and often found in the raw seafood. People who eat raw or undercooked
shell can be infected with this type of bacteria.
The bacteria Vibrio parahaemolyticus infection
will show symptoms after 24 hours. Symptoms appear as watery diarrhea with
abdominal cramps, nausea, fever, vomiting, and shivering. Symptoms can last up
to three days.
More severe infection is rare and infection is
more common in people with weakened immune systems. Infection can be prevented
by cooking seafood until well cooked.
5. Toxoplasma
Most people who suffered toxoplasmosis
infection because of contact with cat feces that carry the parasite, eating raw
meat that has been contaminated or not thoroughly cooked, or drinking water containing
the parasite.
People who develop toxoplasmosis, experienced
flu-like symptoms such as body aches, headache, and fever. But the symptoms are
caused by bacteria toxoplasma very little because the immune system normally
keep your body from infections of this parasite.
These parasites can also cause serious
problems such as damage to the brain, eyes and other organs in pregnant
women and people with weakened immune systems.
To prevent infection due to toxoplasma, cook
food at secure temperatures, wash hands while holding food, drinking sterile
water, and if pregnant, stay away from cat feces.
6. Salmonella
Salmonella is a group of bacteria commonly found in the
avian, eggs, beef, and sometimes on fruits and vegetables which is not washed.
Salmonellosis infections can cause symptoms such as fever, diarrhea, abdominal
cramps and headaches, which can take up to 4 to 7 days.
Most people will recover from the infection
without treatment, but because the bacteria Salmonella infection would have
serious consequences if it occurs in the elderly, babies and people with weak
immune systems.
Children under age 5 are most likely infected
with salmonellosis. If not treated immediately, Salmonella can be
transmitted through the blood to other organs and could be at risk of death.
To prevent infection, avoid eating eggs,
avian, or meat that is raw or half cooked. Raw meat should be kept separate
from other foods to prevent cross-contamination. Wash hands and kitchen
equipment thoroughly after touching uncooked foods.
7. Norovirus
Norovirus is a type of virus that causes gastroenteritis,
a disease that causes inflammation in stomach and intestines. The virus is
usually found in the contaminated food or water but can also be spread through
contact with an infected person.
Gastroenteritis can be highly contagious.
Symptoms include nausea, stomach cramps, vomiting, diarrhea, headache, fever
and fatigue, which can last for several days.
Most people recover from the disease
itself, but for those which is not drink enough fluids to replace what has been
lost because of vomiting and diarrhea, may be required hospital treatment.
To prevent being infected by norovirus, wash
your hands with soap and water and always maintain the cleanliness of the food
you eat.
0 comments:
Post a Comment